Is there a vacuum in double glazing

Discover the benefits of double glazing beyond insulation. Explore soundproofing, enhanced security, and condensation control. Learn about vacuum glazing advancements and making informed choices for energy efficiency and comfort.
Is there a Vacuum in Double Glazing? Exploring Energy Efficiency and Vacuum Glass
Introduction
Double glazing has emerged as a popular solution for homeowners and builders seeking to enhance energy efficiency and comfort in buildings. By providing superior insulation compared to single-pane windows, double glazing has revolutionised the window industry. However, the benefits of double glazing extend beyond insulation alone.
In this article, we will explore the additional advantages of double glazing, focusing on two key areas: soundproofing properties and noise reduction, as well as enhanced security and condensation control. Additionally, we will introduce vacuum glazing, a newer technology that offers potential advantages over traditional double glazing.
While the primary purpose of double glazing is to provide insulation, it also significantly contributes to soundproofing. The combination of two glass panes separated by an insulating layer reduces external noise, creating a more peaceful indoor environment. Furthermore, double glazing enhances security by making it more difficult for intruders to break or penetrate windows, while also controlling condensation, preventing damage to window frames and sills.
As we delve into the realm of double glazing, we will also explore vacuum glazing, which presents advancements in technology. Vacuum glazing involves two glass panes separated by an evacuated space, offering enhanced thermal performance, reduced thickness and weight, and improved soundproofing compared to traditional double glazing.
While vacuum glazing presents notable advantages, it is important to consider factors such as availability and cost-effectiveness. The manufacturing process for vacuum glazing is more complex, which can impact the initial cost. However, the increased cost of vacuum glazing units can be offset by the long-term energy savings they provide.
By understanding the broader benefits of double glazing and exploring the advancements in vacuum glazing, readers will gain valuable insights into the science behind these window systems. This knowledge will empower homeowners, architects, and building professionals to make informed decisions when choosing the most suitable double glazing solutions for their specific needs.
From evaluating energy ratings and industry standards to considering cost-effectiveness and long-term savings, this article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to help readers navigate the world of double glazing. By making informed choices, we can contribute to creating more energy-efficient and comfortable living spaces while reaping the benefits that double glazing brings.
Section 1:
Understanding Double Glazing
Double glazing is a popular solution for enhancing energy efficiency and thermal insulation in buildings. In this section, we will delve into the definition, purpose, and construction of double glazed windows, as well as the significant benefits they offer.
Definition and Purpose of Double Glazing
Double glazing refers to windows that are constructed with two panes of glass separated by a sealed space or gap. The gap between the glass panes acts as insulation, providing a barrier against heat transfer, noise, and weather elements. The primary purpose of double glazing is to improve energy efficiency and thermal performance within buildings.
Benefits of Double Glazing
Double glazed windows offer numerous advantages, making them a preferred choice for homeowners and building occupants. Here are some key benefits:
A. Energy Efficiency
The insulating gap in double glazing helps to reduce heat transfer between the interior and exterior of a building. This results in less reliance on heating and cooling systems, leading to lower energy consumption and reduced utility bills.
B. Thermal Insulation
Double glazed windows provide enhanced thermal insulation, preventing heat from escaping during colder months and reducing heat gain during warmer periods. This helps to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature year-round and reduces the need for excessive heating or cooling.
C. Noise Reduction
The sealed gap in double glazed windows acts as an effective barrier against external noise, creating a quieter and more peaceful indoor environment. This is particularly beneficial for homes located near busy roads, airports, or other sources of noise pollution.
D. Condensation Control
Double glazing helps to minimise condensation build-up on windows by reducing temperature differences between the indoor and outdoor surfaces. This helps to prevent moisture-related issues such as mould growth and damage to window frames.
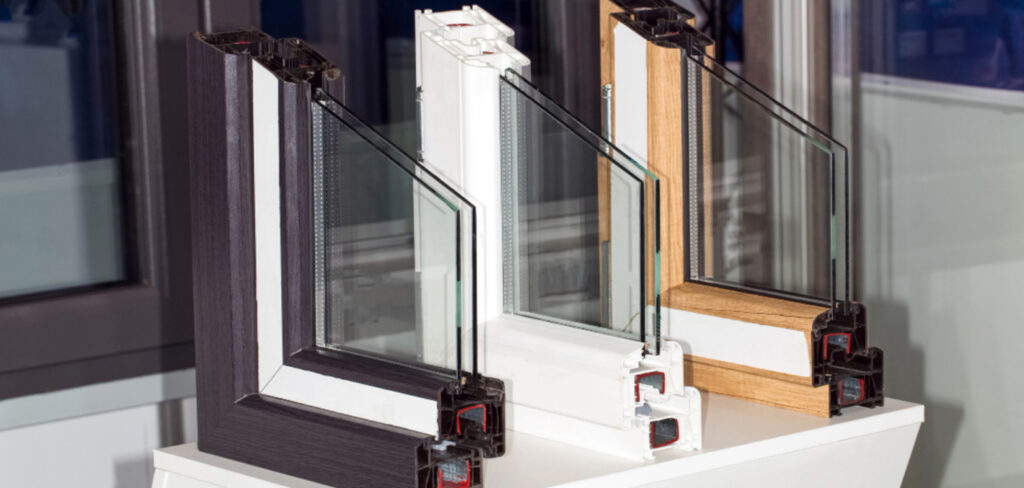
Explaining the Construction of Double Glazed Windows
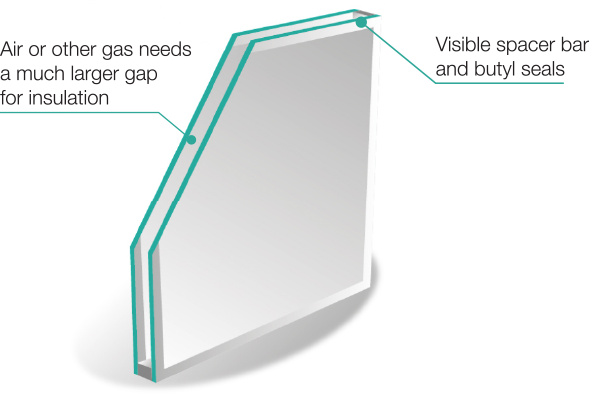
Double glazed windows consist of two glass panes that are separated by a spacer bar. The spacer bar creates the sealed space or gap between the panes, which is often filled with air or a specialised insulating gas, such as argon or krypton. The sealed unit is then securely sealed and installed within the window frame.
The glass panes used in double glazing can be coated with a low-emissivity (low-E) coating. This coating helps to reflect heat back into the room while allowing natural light to enter. Additionally, some frames of double glazed windows are designed to provide optimal insulation and minimise heat transfer through the window edges.
By understanding the definition, purpose, and construction of double glazing, we can appreciate the significant benefits it offers in terms of energy efficiency, thermal insulation, noise reduction, and condensation control. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into specific aspects of double glazing to provide a comprehensive understanding of this innovative solution for improving building performance.
Section 2:
The Gap in Double Glazing
In double glazed windows, the gap between the glass panes plays a crucial role in enhancing insulation and overall performance. In this section, we will explore the characteristics of the gap, debunk the myth of a vacuum, and shed light on the role of air or inert gases within this space.
Exploring the Gap Between the Glass Panes:
The gap between the glass panes in double glazed windows is carefully designed to provide optimal insulation. While the exact width of the gap may vary depending on factors such as window type and energy efficiency requirements, it typically ranges from 6 to 20 millimeters.
Debunking the Myth of a Vacuum
Contrary to common misconceptions, the gap in double glazing is not a vacuum. Instead, it is filled with air or an inert gas, such as argon or krypton. These gases are chosen for their higher density compared to air, which helps to reduce heat transfer and improve insulation.
Understanding the Role of Air or Inert Gases
The air or inert gases present within the gap act as insulating barriers, limiting the conduction of heat between the interior and exterior of a building. While air is a common and effective insulator, inert gases provide even better insulation due to their higher density and lower thermal conductivity.
Argon and krypton are often used as insulating gases in double glazed windows. These gases have a significantly lower thermal conductivity than air, reducing heat transfer and improving the overall thermal performance of the window.
It is important to note that the choice of gas and the width of the gap depend on various factors, including regional climate conditions, energy efficiency regulations, and desired performance levels. Professional window manufacturers and suppliers can provide guidance on selecting the appropriate gas and gap width based on specific requirements.
By understanding the characteristics of the gap in double glazing and debunking the myth of a vacuum, we can appreciate the role of air or inert gases in enhancing insulation and energy efficiency. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into insulation materials, funding opportunities, and best practices for retrofitting energy-efficient insulation, providing valuable insights for architects and local authority professionals seeking to optimise building performance in the UK.
Section 3:
Insulation Materials in Double Glazing
When it comes to double glazed windows, the choice of insulation materials plays a crucial role in determining their effectiveness in terms of energy efficiency and soundproofing. In this section, we will provide an overview of common insulation materials used in double glazed windows, compare their effectiveness, and consider their impact on energy efficiency and soundproofing.
A. Overview of Common Insulation Materials
There are several insulation materials commonly used in the construction of double glazed windows. These include:
Glass
Glass itself acts as a natural insulator, providing a barrier against heat transfer. It is a widely used material due to its transparency and durability.
Low-E Coatings
Low-E (Low-Emissivity) coatings are thin metallic layers applied to the glass surface. They help to reduce heat transfer by reflecting thermal radiation while allowing visible light to pass through.
Argon or Krypton Gas
As mentioned earlier, these inert gases are often used to fill the gap between the glass panes in double glazed windows. Their low thermal conductivity enhances insulation by minimising heat transfer.
Insulating Foam
Some double glazed windows incorporate insulating foam within the frames. This foam provides an additional layer of insulation, further reducing heat conduction.
More reading on Insulated Glazing: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulated_glazing
B. Comparing Effectiveness of Insulation Materials
Each insulation material mentioned above offers varying levels of effectiveness in terms of energy efficiency and soundproofing. Low-E coatings, for example, significantly reduce heat loss or gain by reflecting infrared radiation back into the room. Argon or krypton gas, on the other hand, minimizes heat conduction through the gap between the glass panes.
It’s important to note that the combination of these insulation materials, such as using low-E coatings in conjunction with argon or krypton gas, can enhance the overall performance of double glazed windows.
C. Impact on Energy Efficiency and Soundproofing
The choice of insulation materials directly affects the energy efficiency and soundproofing capabilities of double glazed windows. By reducing heat transfer, these materials help maintain a more consistent indoor temperature, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower heating or cooling costs.
Additionally, the insulation properties of double glazed windows contribute to improved soundproofing, minimising external noise and creating a quieter and more peaceful indoor environment.
When selecting insulation materials for double glazed windows, it is essential to consider factors such as climate conditions, building regulations, and specific requirements for energy efficiency and soundproofing. Consulting with experts in the field can provide valuable guidance in choosing the most suitable insulation materials for your specific needs.
In the upcoming sections, we will explore the factors that significantly impact the performance of double glazed windows. We will discuss the importance of proper installation and sealing to prevent thermal leaks and address common challenges and misconceptions associated with double glazing. By understanding these factors, you can make informed decisions and ensure optimal performance and benefits from your double glazed windows.
Section 4:
Factors Affecting Double Glazing Performance
Double glazed windows offer numerous benefits in terms of energy efficiency, thermal insulation, and soundproofing. However, several factors can significantly impact their overall performance. By understanding these factors, you can make informed decisions and ensure optimal performance and benefits from your double glazed windows.
A. Quality of Installation and Sealing
Proper installation is crucial for the effectiveness of double glazed windows. A professional installation ensures airtightness and minimises thermal leaks. Common issues related to improper installation include gaps, inadequate sealing, and poor alignment. It is essential to select experienced installers who follow industry best practices to maximise the performance of your double glazed windows.
B. Glass Thickness and Configuration
The thickness and configuration of the glass play a vital role in insulation and soundproofing properties. Thicker glass provides better insulation, reducing heat transfer and external noise. Different glass types, such as laminated, tempered, or low-emissivity (Low-E) glass, offer specific benefits. Consider your specific needs and climate conditions when selecting the appropriate glass thickness and configuration for your double glazed windows.
C. Frame Material and Design
The frame material and design impact both the aesthetics and performance of double glazed windows. Common frame materials include uPVC, aluminum, and timber. Each material has different thermal conductivity properties and durability. Additionally, consider the architectural style and maintenance requirements when selecting the frame design to ensure compatibility with your overall design scheme.
D. Gas Filling and Spacer Systems
Double glazed windows often have a gap between the glass panes that is filled with an inert gas like argon or krypton. These gases improve thermal insulation by reducing heat transfer. The quality of the gas fill and the spacer system that maintains the integrity of the gas fill are essential for long-term performance. Warm-edge spacers are increasingly used to enhance energy efficiency by minimising heat loss at the edges of the glass panes.
E. Maintenance and Care
Proper maintenance and care are crucial to ensure the longevity and performance of double glazed windows. Regular cleaning and inspection help to identify and address issues promptly. Common issues that may arise include condensation, fogging, or seal failure. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for cleaning and maintenance practices to preserve the energy efficiency and functionality of your double glazed windows.
By considering these factors and making informed choices, you can maximise the energy efficiency, thermal insulation, and soundproofing capabilities of your double glazed windows. Investing in high-quality materials, professional installation, and regular maintenance will contribute to the long-term performance and comfort of your living space.
Section 5:
Benefits Beyond Insulation
In addition to its primary role as an effective insulation solution, double glazing offers several other notable benefits that can enhance the comfort, safety, and overall quality of a building. This section will explore two significant advantages of double glazing beyond insulation: soundproofing properties and noise reduction, as well as enhanced security and condensation control.
A. Soundproofing Properties and Noise Reduction
One of the most significant advantages of double glazing is its soundproofing properties. The combination of two glass panes separated by an air or gas-filled space acts as an effective barrier against external noise. This is especially beneficial for buildings located in busy urban areas, near highways, airports, or other noisy environments.
The insulating layer of air or gas within the double-glazed unit helps to minimise sound transmission by absorbing and reducing sound waves. When compared to single-pane windows, double glazing can significantly reduce noise levels, creating a quieter and more peaceful indoor environment. This is particularly advantageous for residential buildings, hotels, schools, hospitals, and any other spaces where noise control is crucial for occupant comfort and concentration.
B. Enhanced Security and Condensation Control
Another advantage of double glazing is its contribution to enhanced security and condensation control. The construction of double-glazed windows makes them more difficult to break or penetrate compared to single-pane windows. The presence of multiple glass panes, along with the interlayer of gas or air, adds an extra layer of protection against forced entry, increasing the overall security of a building. This can be especially important for ground-level windows, vulnerable areas, or properties that require heightened security measures.
Furthermore, double glazing helps to reduce condensation on window surfaces. Condensation occurs when warm, moist air comes into contact with a cold surface, causing water droplets to form. The insulating properties of double glazing prevent the inner pane from becoming too cold, reducing the likelihood of condensation forming on the glass. By minimising condensation, double glazing helps maintain a clearer view through the window and reduces the potential for mould growth and damage to window frames and sills.
In conclusion, double glazing offers benefits beyond its primary role as an insulation solution. Its soundproofing properties and noise reduction capabilities make it an excellent choice for buildings situated in noisy areas. Additionally, the enhanced security features and condensation control provided by double glazing contribute to a safer and more comfortable indoor environment. These additional benefits make double glazing a valuable investment for both residential and commercial buildings, offering improved quality of life for occupants.
Section 6:
Vacuum Glazing: Advancements in Double Glazing Technology
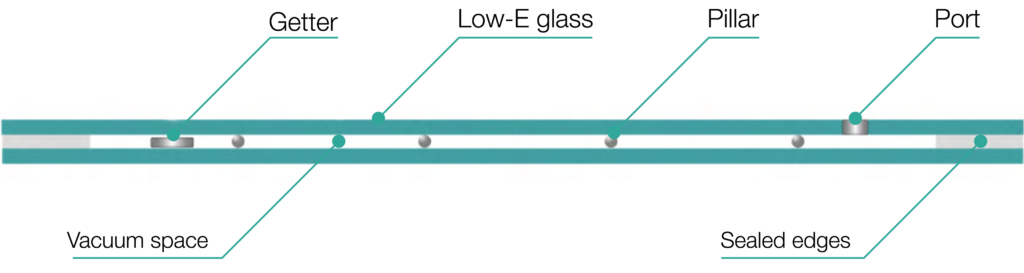
In recent years, advancements in double glazing technology have led to the development of vacuum glazing, which offers several advantages over standard double glazing. Vacuum glazing consists of two glass panes that are separated by a thin, evacuated space instead of being filled with air or gas. This section will explore the benefits of vacuum glazing and its potential advantages over traditional double glazing.
A. Enhanced Thermal Performance
Vacuum glazing offers superior thermal insulation compared to standard double glazing. The absence of air or gas between the glass panes eliminates convective heat transfer, which is a significant source of heat loss in traditional double glazing. As a result, vacuum glazing can provide even higher levels of thermal efficiency, reducing heat transfer and maintaining a more comfortable indoor environment.
B. Reduced Thickness and Weight
Another advantage of vacuum glazing is its reduced thickness and weight. Since there is no gas or air filling the space between the glass panes, vacuum glazing can be significantly thinner compared to standard double glazing. This thinner profile makes it an ideal choice for retrofitting projects, where window frame sizes may not accommodate thicker double-glazed units. Additionally, the reduced weight of vacuum glazing makes it easier to handle and install, providing practical benefits during the construction or renovation process.
C. Improved Soundproofing
Vacuum glazing also offers enhanced soundproofing properties. The absence of air or gas between the glass panes reduces sound transmission, resulting in better noise reduction compared to traditional double glazing. This is particularly beneficial for buildings located in noisy environments, where maintaining a quiet indoor space is essential.
D. Potential Downsides and Considerations
While vacuum glazing presents several advantages, it is important to consider a few factors. Firstly, vacuum glazing is a relatively newer technology, and its availability may be limited compared to standard double glazing options. The manufacturing process for vacuum glazing is more complex, involving specialized techniques and equipment, which can impact the cost of these units. It is crucial to evaluate the initial investment and compare it with the potential long-term savings associated with vacuum glazing before making a decision.
Although the upfront cost of vacuum glazing units may be higher than that of traditional double glazing, it’s important to consider the energy savings over time. The enhanced thermal performance of vacuum glazing can significantly reduce heating and cooling costs, leading to substantial long-term savings on energy bills. These energy savings can help offset the initial investment, making vacuum glazing a cost-effective choice in the long run.
Conclusion
In conclusion, double glazing in its various forms offers numerous benefits for energy efficiency, comfort, soundproofing, security, and condensation control. While vacuum glazing presents advancements in technology with its enhanced thermal performance, reduced thickness and weight, and improved soundproofing, it is essential to consider factors such as availability and cost-effectiveness.
The availability of vacuum glazing may be more limited compared to standard double glazing options due to its relatively newer technology. Additionally, the more complex manufacturing process of vacuum glazing can impact the initial cost of these units. However, it is important to evaluate the long-term savings associated with energy efficiency and consider the potential return on investment.
By evaluating energy ratings, industry standards, and conducting a cost-effectiveness analysis, one can determine the most suitable option for a particular project. Understanding the benefits and considerations of both traditional double glazing and vacuum glazing enables homeowners, architects, and building professionals to make informed decisions that balance their specific needs and budget.
In the end, the choice between standard double glazing and vacuum glazing will depend on various factors, including project requirements, availability, and cost-effectiveness considerations. By considering these factors and understanding the long-term savings potential, individuals can choose the most suitable double glazing solution to achieve optimal energy efficiency and comfort in their buildings.
Find out more about our vacuum glazing products:
Heritage Vacuum Insulated Glass
Enhance Vacuum Insulated Glass